Single Sign-On (SSO) is a service which allows users to have one set of login credentials to access multiple web applications. SSO allows a user to log in once and gain access to various applications, without the need to re-enter login credentials at each application.

SSO works as follows:
A user requests access to an application, this request is forwarded to a Service Provider where the user is asked for credentials (for example “Sign in with Google” or “Sign in with Facebook,”). Once the credentials are entered, the Service Provider will verify the credentials and authorise the user. The authorisation token is sent to the web application, and this will be used to authorize the user on the web application too. Some SSO providers might also provide additional information to the web application, such as the user’s Name, Surname and email address.
SSO authentication is supported by Acunetix and the redirect from the application being scanned to the SSO Service Provider will be followed in the Login Sequence Recorder (LSR) for authentication purposes.
For example, if the web application (the Target) being scanned is Site A, and the authentication page is at Site B, you will need to record a Login Sequence that will navigate to Site A and record the actions required to login. In the process, you will be redirected to Site B, where you will need to proceed with the login. After logging in, you will be directed back to Site A, where you can proceed with setting up any Restricted links and the Session Pattern.
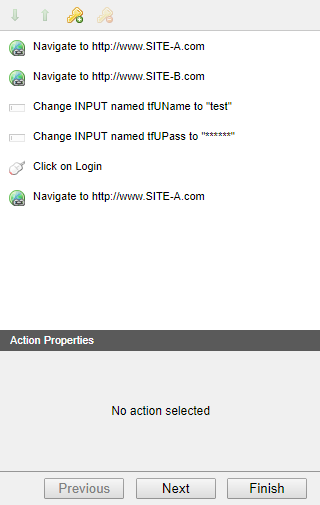
Once the Login Sequence is configured we recommend playing back the recorded steps ensuring that the Authentication flow is being followed correctly.
You can verify that the scanner is successfully logging in by navigating to the Site Structure and validate that authenticated paths are being crawled.
Get the latest content on web security
in your inbox each week.



